|
Image Example
|
Artistic Manifestations
|
Artists
|
Artistic Representations
|
 Jean-Honore Fragonard
|
|
|
Portraits (single, group, including backgrounds
Narratives, social statements, satire |

|
|
|
Portraits- single, group. including backgrounds
Narratives - historical, genre Historical metaphors - classical reference |

Francisco Goya
|
|
|
Portraits - single, group; including settings and backgrounds
Narrative - literary, historical Landscape -objective, subjective and sublime Architecture -Gothic Revival |

|
Direct observations of society and nature
Development of political and social satire Social and political cartoons and caricatures Social observations,emphasis on class distinctions Natural atmospheres |
France:
|
Portraits - single, group, including settings and backgrounds
Animals - settings, with and without people Narrative - objective, subjective, satire, literary Landscape - as a subject, as a background |

|
|
Artists: France Edouard Manet (1832-1883) Edgar Degas (1834-1917) Berthe Morisot (1841-1895) Claude Monet (1840-1926) Auguste Renoir (1841-1919) Auguste Rodin (1840-1917) |
Artistic Representations: Portraits (single, group; exterior and interior backgrounds) Landscape (as a subject) Narrative (genre, leisure, entertainment) |

|
Artistic Manifestations: Diverse individual characteristics, yet influenced by Impressionist artists Color theories examined Bright colors; visible distinct brushwork Color separations Clearly defined edges Two manifestations: Formal structure and values: composition paramount Cezanne, Seurat Emotional Content Van Gogh, Gauguin Influence of Japonism |
Artists: France Henri de Toulouse Lautrec (1864-1901) Paul Cezanne (1839-1906) Paul Gauguin (1848-1903) George Seurat (1851-1891) Vincent Van Gogh (1853-1890) |
Artistic Representations: Portraits (self, individual, group) Figure Studies (formal structure vs. emotional content) Still lifes Narratives (religious, metaphors) |

Kathe Kollwitz The Uprising, 1899 |
Artistic Manifestations: Expressive and emotional possibilities of color Introduction of Freudian theory Symbolist content: Social consciousness of realism Internal world of imagination Irrational aspects of the human mind Subject matter: Literature Myths Allegory Dreams Spirituality Haunting, stark imagery |
Artists: France: Henri Rousseau (1844-1910) Edvard Munch 1863-1883) (born Norway) Germany: Kathe Kollwitz (1867-1945) Emil Nolde (1867-1956) Ernst Kirchner (1880-1938) Max Beckman (1884-1950) George Grosz (1893-1959) Austria: Gustave Klimt (1862-1918) |
Artistic Representations: Portrait (self, group) Psychological content Backgrounds Figures (narrative, decorative) |

Franz Marc Der Tiger, 1914 Lenbachhaus; Munich, Germany |
Artistic Manifestations: Bright, non-naturalistic, and often unusually vivid colors Strong use of pictorial space, pictorial movement Forms built from color and/or pattern Emotional content |
Artists: France: Henri Matisse (1869-1954) Georges Rouault (1871-1958) Maurice de Vlaminck (1876-1958) Andre Derain (1880-1954) Germany: Franz Marc (1880-1916) |
Artistic Representations:
Figures Landscapes Animals |
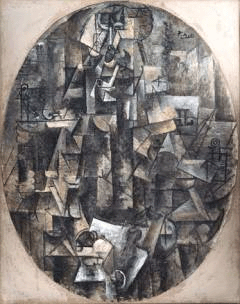 Pablo Picasso Man With a Pipe, 1911 Kimball Art Museum; Fort Worth, Texas |
Artistic Manifestations: Objective Radical approach to space, spatial organization Radical break from reality: Abstraction Fragmentation Distortion Simplification Asymmetry Simultaneous views and directions. No single point of view Bold strokes of color or monochromatic schemes |
Artists: France: Jacques Villon (1875-1963) Pablo Picasso (1880-1973) Georges Braques (1881-1963) Fernand Leger (1881-1955) |
Artistic Representations: Figures Still lifes |

Giacomo Balla Dynamism of a Dog on a Leash, 1912 Jewish Museum; New York City |
Artistic Manifestations: Dynamism, strong compositions Dynamic energy Speed, travel Technology Machines Strong color Break with academic traditions |
Artists: Italy: Giacomo Balla (1871-1958) Filippo Marinetti (1876-1944) Umberto Boccioni (1882-1916) Gino Severini (1883-1966) |
Artistic Representations: People (usually single) Citylife Sports Aeropaintings (depicting movement) Text (words) in art |

Paul Klee Temple Gardens, 1920 Metropolitan Museum of Art; New York City |
Artistic Manifestations: Correlation between creative design and modern industry and science Smooth, tensile forms combined with strong colors (ex. tubular steel furniture) Integrated expressionist styles with design and architecture Materials: steel, concrete, chrome, glass Varied Fine and Technical artists, architects: Advertising, stage, photography, typography, furniture, architecture |
Artists: (most emigrated after the Nazis closed the Bauhaus in 1933) Germany Lyonel Feininger (1871 – 1956) Walter Gropius (1883 – 1969) Ludwig Mies van der Rohe (1886 – 1969) Josef Albers (1888 – 1976) Switzerland Paul Klee (1879 – 1940) |
Artistic Representations: Abstract imagery Advertising, typography Industrial design: furniture, house-wares Architecture |

Salvador Dali Persistence of Memory, 1931 Metropolitan Museum of Art; New York City |
Artistic Manifestations: Symbolism, personal imagery Alternative to formal theories of Cubism Emphasis on positive expression Influenced by theories of Sigmund Freud Reunited ‘conscious and unconscious’ realms of experience ‘Absolute Reality:’ the worlds of dream and fantasy joined to the everyday rational world in an “absolute reality, a surreality” |
Artists: France Marc Chagall (1887 – 1985) Marcel Duchamps (1887 – 1968) Max Ernst ( 1891 – 1976) Yves Tanguy (1900 – 1955) Spain Joan Miro (193 – 1983) Salvador Dali ( 1904 – 1989) Belgium Rene Magritte (1898 – 1967) Italy Giorgio de Chirico (1888 – 1978) |
Artistic Representations: Spontaneous imagery, free association Automatism Fantasy Confusion |